Article list
#UMED-LAB-002 SUMMARY The living lab methodology has been enriched with elements of value-based health care and patient-centered care approaches. It shifts its focus from merely testing new solutions to ensuring delivery of tangible health outcomes that matter most to patients. Patients are not passive subjects within the innovation process, but directly shape the development, implementation,…
#UMED-LAB-001 SUMMARY A state-of-the-art research laboratory providing in vivo and in vitro studies on animal models and cell lines in compliance with international standards (GLP, ISO 17025:2018-02), supporting the development of pharmaceutical and biomedical sciences BACKGROUND Animal Research Facility of the Faculty of Pharmacy, Medical University of Lodz, is a certified research center conducting experimental…
#UZSM-004 SUMMARY The collection includes human left ventricular myocardial samples of failing hearts collected freshly after heart transplantation or left ventricular device implantation in Croatia. Several myocardial samples are from donors without known heart disease. Samples were freshly frozen after harvesting and stored at -80 °C. BACKGROUND The samples are used for research purposes, including…
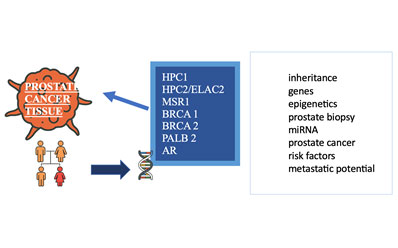
#UZSM-003 SUMMARY The collection includes formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue of breast cancer, prostate cancer, renal cell carcinoma and colorectal cancer, as well as testicular germ cell tumors. BACKGROUND The collections were sampled and stored because of different studies and now can be used for research purposes, including analysis of the tumor histology, protein expression,…
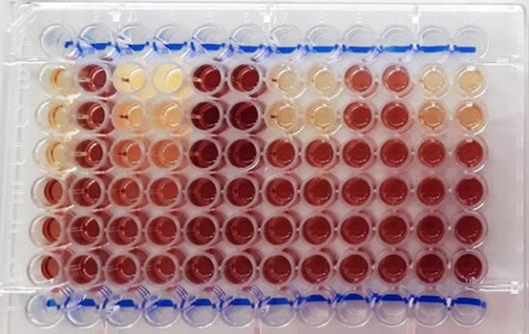
#UZSM-002 SUMMARY Cytotoxicity testing of new chemical entities and biological extracts against various cell lines. BACKGROUND Cytotoxicity testing is used in drug discovery projects to evaluate the safety profile of new substances. Cytotoxicity testing ensures determination of inhibitory concentrations of novel chemical entities and biological extracts, IC50, that inhibit the growth of cells in a…
#UZSM-001 SUMMARY Standardized antibacterial susceptibility testing of new chemical entities and biological extracts against standard and typed major bacterial pathogens. BACKGROUND Antibacterial susceptibility testing is used in drug discovery projects to evaluate the activity of new substances against target bacterial pathogens. Standardized antibacterial susceptibility testing ensures determination of minimal inhibitory concentrations of novel chemical entities…
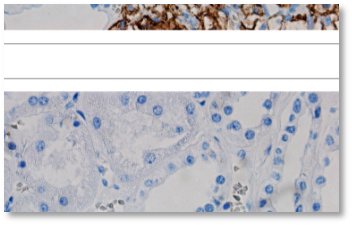
#ULMF-001 SUMMARY The collection includes primary skeletal muscle cells (HSMCs) obtained from skeletal muscle tissue (m. semitendinosus) obtained as surgical waste during standard anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction in subjects with ACL rupture. No tissue was harvested solely for research purposes. BACKGROUND Primary HSMCs (myoblasts and/or myotubes) are used as an in vitro model for…
#BMC-003 SUMMARY These antigens are suitable for the serological detection and screening of infections caused by various Chlamydia species. BACKGROUND Chlamydia species are obligate intracellular bacteria that can infect humans and animals, often causing respiratory or reproductive diseases. Surveillance of different chlamydial infections is crucial for assessing disease burden, implementing public health interventions, and preventing…
#BMC-002 SUMMARY Phase I and Phase II antigens of C. burnetii are essential for confirming Q fever infection and monitoring therapeutic outcomes in both humans and animals. BACKGROUND Q fever is an acute or chronic disease caused by the obligate intracellular Gram-negative bacterium Coxiella burnetii. This pathogen is primarily transmitted to humans through inhalation of…
#CEITEC MU-003 SUMMARY Method to increase plant resistance to abiotic stress, particularly drought and soil salinity, by upregulating DIR13 gene expression. BACKGROUND Abiotic stresses like drought and salinity significantly impact crop yields. Climate change exacerbates these challenges, necessitating innovative solutions. This invention focuses on enhancing plant resilience through genetic means. FEATURES AND KEY BENEFITS REFERENCES…


